Step 3: Legal, Technical & Spatial Considerations
Part of
Keywords
We have combined the Technical, Legal, and Spatial aspects of the OSCM toolkit in one STEP 3 as they are so closely interrelated. All these three elements need to work together and in parallel guided by an ethical framework to effectively address social values and privacy by design principles to insure digital rights.
3.0.1 – Dilemma Diagram
The Legal, Technical, and Spatial aspects of crowd monitoring projects are all interrelated and all require serious ethical considerations. In order to better understand this complexity, we have visualized these interrelations in a Venn diagram that places Ethics at the center.
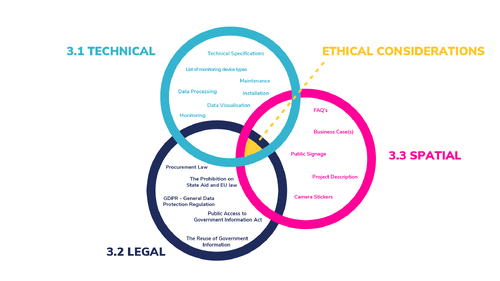
3.0.2 – Applying an Ethical Framework
At this point, it is important to take a step back to get an overview of the ethical considerations involved to effectively address the social values involved in your crowd monitoring project and apply a methodology to measure strengths and weaknesses with key stakeholders.
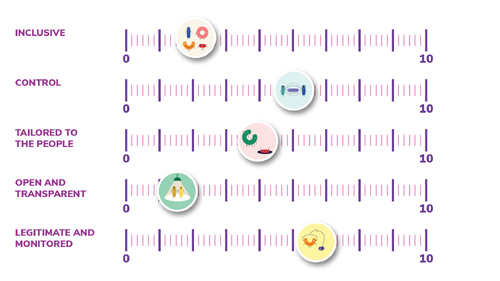
Inclusive
Our digital city is inclusive. We take into account the differences between individuals and groups, without losing sight of equality.
Control and Tailored To The People
Data and technology should contribute to the freedom of citizens. Data are meant to serve the people. To be used as seen fit by people to benefit their lives,
to gather information, develop knowledge and find room to organise themselves. People stay in control over their data.
Open and Transparent
What types of data are collected? For what purpose? And what are the outcomes and results? We are transparent about this.
Legitimate and Monitored
Citizens and users have control over the design of our digital city. The government, civil society organizations and companies facilitate this. They monitor the development and the social consequences.
From Everyone For Everyone
Data that the city, companies and other organizations generate from the city are held in common. Everyone can use them. Everyone can benefit from them. Together we make agreements about this.
3.0.3 – Measuring Ethical Principles
We suggest that at this stage you hold an ethics workshop to apply a methodology to measure ethical principles related to the Legal, Technical, and Spatial considerations of your project. In Amsterdam we have used the TADA principles and workshop with success, consider using this format or source a data ethics workshop in your city.
3.1.1 – Legal Compliance
In Europe, GDPR compliance guided by Privacy by Design principles are where to begin when you start gathering and understanding all the information you need to start a legally responsible crowd monitoring project.
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
(AVG – Algemene Verordening Gegevensbescherming)
The GDPR is the umbrella reference for all EU member states regarding regulations for any organization that targets or collects data related to people. It’s very important to comply with the new EU law for data privacy in every way as the fines for violations can be very heavy. It’s complicated, but The Guide to GDPR Compliance is a good place to get familiar with regulations that you need to consider in the beginning phases of your OSCM camera vision project.
IMPORTANT: In order to make sure you are GDPR compliant you should complete the GDPR Compliance Checklist https://gdpr.eu/checklist/
Other Useful Links: https://gdpr.eu (English) and how-to-make-your-business-gdpr-compliant (English), privacy-en-persoonsgegeven (Dutch)
3.1.2 – Privacy By Design
The privacy by design framework is an engineering design approach which calls for privacy to be taken into account throughout the whole engineering process. The concept is an example of value sensitive design, i.e., to take human values into account in a well-defined manner throughout the whole process. In general it is a seven step process framework to guide the design process.
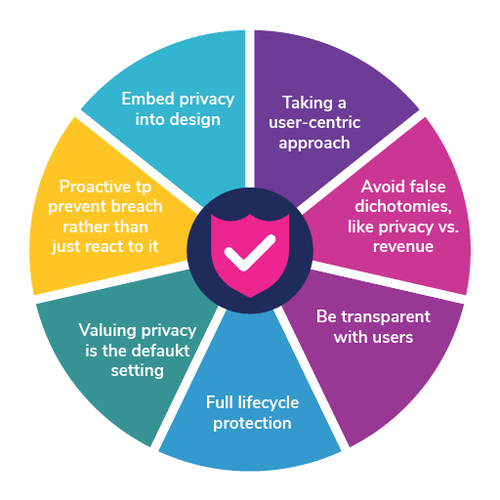
More Specifically, Privacy by Design is a key regulation in the GDPR as described in Article 25: Data Protection by Design and by Default.
For general information about Privacy by Design as a framework visit: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Privacy_by_design
For specific information about Privacy by Design as a regulation in the GDPR visit:
https://gdpr-info.eu/art-25-gdpr/
3.1.3 – Legal Compliance Overview
Among several laws, procedures, documents and ethical principles you must consider before moving forward you needed to make sure you are familiar with the specific legal aspects of crowd monitoring in public spaces in your country, region, and city. For OSCM projects in the EU and the Netherlands here is a list of items we know are important from our experience. For full details download the Legal Resource Library PDF.
See below for more resources:
| Name | Useful Links | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| European Data Protection Officer (DPO) | /data-protection-officeer-en | ||
| The Dutch Data Protection Authority (DPA) | https://autoriteitpersoonsgegevens.nl/en | ||
| Right to Erasure Form (Part of GDPR) | https://gdpr.eu/right-to-erasure-request-form/ | ||
| IoT registration (Amsterdam) | https://slimmeapparaten.amsterdam.nl/about
|
||
| Video Camera Registration (Amsterdam) | https://www.amsterdam.nl/privacy/camera’-sensoren/ | ||
| AI Register (Amsterdam) | https://algoritmeregister.amsterdam.nl/en/ai-register/ | ||
| Legally required signs and stickers (Amsterdam) | https://slimmeapparaten.amsterdam.nl/about/faq | ||
| Project Description | https://slimmeapparaten.amsterdam.nl/about/faq |
Additional General Legal considerations that will vary greatly by region and use case.
- Governance, ownership and responsibilities
- Contracts and liability
- Open Data publishing, use, and reuse compliance issues (EU)
3.2 – Technical
As technology grows, so does the number and complexity of sensors and devices that can be used to monitor public space. The technical choices you make will relate to decisions made in the previous steps when you established your goals, use case and planned your project accordingly. What is important in this step is that you first familiarise yourself with the different options available and then take a closer look at the Degrees of Invasiveness to help guide a responsible and ethical decision.
Computer Vision
Current computer-vision systems do a decent job at classifying images and localizing objects in photos, when they’re trained on enough samples but it takes a lot of work to achieve a high level of accuracy. Computer vision applications include facial and object recognition, also biometrics which can be very invasive.
More about Computer_vision
CCTV
An acronym for Closed Circuit Television, CCTV has been around for a while and is used mostly for security purposes. It’s all about recording video footage of people either in public or private spaces and can be applied to computer vision applications but not necessarily. Also known as video surveillance, it is perhaps the most invasive technology you can use.
More about Closed-circuit_television
Sound Sensors
These come in all shapes and sizes. They can record sound or just detect it. They can be highly accurate and measure volume (dbl), tone, pitch, and/or frequency or simply detect the existence sound above a certain threshold. They all use microphones but not all deliver insights related to the nature of sound or sound identification which is enabled by using existing libraries or training using machine learning.
More about sound-sensor
Thermal
Or Thermal Imaging Cameras used for crowd monitoring use infrared technology to measure object radiation and vary greatly in range and accuracy, from detecting the existence of a person at night at long range to a fairly accurate temperature reading at close range.
Mobile App
Convenient because almost everybody has a Smart Phone with them wherever they go but also problematic depending on what you want to achieve. Geolocation services, Bluetooth, Wifi, and/or Mobile Data must be on for instance depending on the application.
More about Mobile App data
Motion Sensors
Or Motion Detectors can be one of several technologies including Passive Infrared (PIR), Microwave, Sonar, and Ultrasonic. Although this technology is useful to detect single object presence, iit is not effective for multiple objects or crowds in large spaces.
More about Motion_detectors
Millimeter Wave
Or high resolution radar uses an ultra high frequency radio wave to detect, locate, and track moving targets with a very high level of accuracy but with a limited distance. This technology is also used for security screening to detect weapons and other dangerous objects under clothing.
More about Millimeter Wave
WiFi Sniffer
Also known as a packet sniffer. This technology detects smart phones on Wifi mode searching for networks. The sniffer intercepts probe requests and the MAC address of the device making it useful to track an individual in a large space but also potentially invasive.
More about WiFi_Sniffers
3-D Sensors
A depth sensing technology that uses three different techniques to detect and image map objects: stereoscopic vision, structured light pattern, or time of flight (ToF). All capture or produce 3-D images which are anonymous and trackable in crowded spaces with a high level of accuracy.
More about 3-D sensors
3.2.1 Technical – Degrees of Invasiveness
Different crowd monitoring technologies have their own degree of invasiveness depending on how they are used and where. You should be aware of how different sensors and devices can compromise privacy and compare them to others to understand your options.
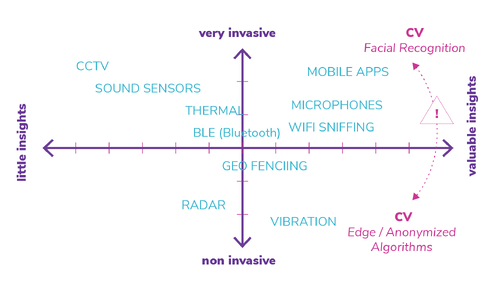
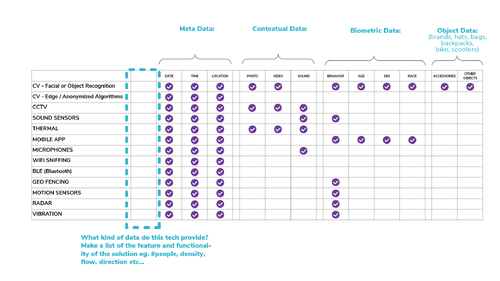
3.2.2 Technical – Invasiveness Matrix
A quick guide to the various kinds of data that different crowd monitoring technologies generate. The Invasiveness Matrix will tell you what solutions will create biometric data versus anonymous data, location data and more.
The NYC IoT Strategy – Example of Assessing Privacy Risk
3.3 Spatial
Different spaces have different requirements when designing and implementing a sensor project. We have crated a simple example with six spatial categories and specific considerations. Below you will find these considerations and some important questions you need to ask yourself and your team.
In Amsterdam it is compulsory for all data gathering devices or sensors to be registered. Make sure you follow the requirements in your city. For more information in Dutch: https://www.amsterdam.nl/nieuws/nieuwsoverzicht/meldplicht-dataverzamelaars/
Signage:
Does your project area have signage, boards, or flags to inform public that they are in a monitoring zone?
Privacy:
Does your project area provide the public the right to be invisible or anonymous? How so?
Permission:
Do you need permission from property or facility manager? In public space, you’ll need specific permissions or exceptions from the municipality.
Agreements:
Do you need data processing agreement, data protection or any other regulatory requirements?
Registration:
Should the cameras, project documents or FAQ’s need to be registered?
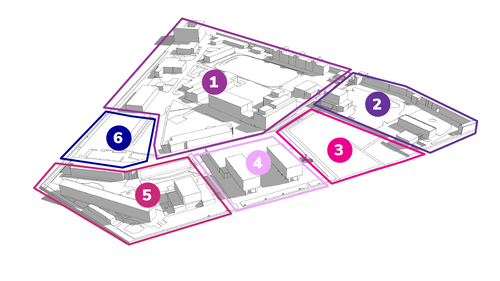
In this example we are using the Marineterrein Amsterdam Living Lab – Inner-city test ground for a sustainable living environment. This 1/2 square mile district is a wonderful microcosm of any city space, function or activity. For more info: https://www.living-lab.nl
Private Property
Cities are mostly made up of private properties. Owners of these properties control access and can only collect data from visitors for security reasons.
| Considerations | |
|---|---|
| Permission | |
| Agreements | |
| Registration | |
| Signage | |
| Privacy |
Public Parks
City parks are owned or managed by the local municipality. You’ll need special permission from authorities to collect data from these areas.
| Considerations | |
|---|---|
| Permission | ✔︎ |
| Agreements | ✔︎ |
| Registration | ✔︎ |
| Signage | ✔︎ |
| Privacy | ✔︎ |
Waterfronts & Harbors
Mixed management between the city, water authorities and sometimes private boating clubs or marinas. Collecting data needs to be approved by every stakeholder
| Considerations | |
|---|---|
| Permission | ✔︎ |
| Agreements | ✔︎ |
| Registration | ✔︎ |
| Signage | ✔︎ |
| Privacy | ✔︎ |
Campus & Business Parks
Hospitals, universities, commercial or industrial properties are mostly private. Collecting data is usually permitted by facility management or the owner.
| Considerations | |
|---|---|
| Permission | ✔︎ |
| Agreements | |
| Registration | |
| Signage | |
| Privacy |
Hotels, Bars & Restaurants
Cafes, courtyards and terraces are usually private property. Owners of these properties can collect data of their customers with consent.
| Considerations | |
|---|---|
| Permission | ✔︎ |
| Agreements | |
| Registration | |
| Signage | ✔︎ |
| Privacy | ✔︎ |
Sports Grounds & Recreation
Clubs, pitches, playgrounds or stadiums can be mixed between private and public ownerships. Collecting data of guests should be for legitimate safety reasons.
| Considerations | |
|---|---|
| Permission | ✔︎ |
| Agreements | ✔︎ |
| Registration | ✔︎ |
| Signage | ✔︎ |
| Privacy | ✔︎ |
Image credits
Icon image: justbynat - paars



